Scanning tunneling Microscope (STM)
Introduction
Gerd binning & Heinrich Roher invented the STM in 1981 and won the Nobel prize in physics in 1986.
Definition
A scanning tunneling microscope (STM) is a device that obtains images of the atoms on the surfaces of materials. The resolution of the image is on the order of one nanometer (1 nm) or less, 1nm=0.000000001 meter=
USES
STM is used to see individual atoms on the surface of a sample in 3-D. This technique is used to study things such as conductive materials, even DNA molecules. It is an instrument for imaging surface at atomic level.
Principle
STM is based on the principle of quantum mechanism e tunneling i.e., if a flat surface of metals are separated by an insulator or vacuum, the electron in the material can't transfer from one surface to another through the insulator due to energy barrier. But if a voltage is applied between the two surfaces, then a driving force acts for electron to move across the barrier by tunneling and a small current flows when the distance between is very small.
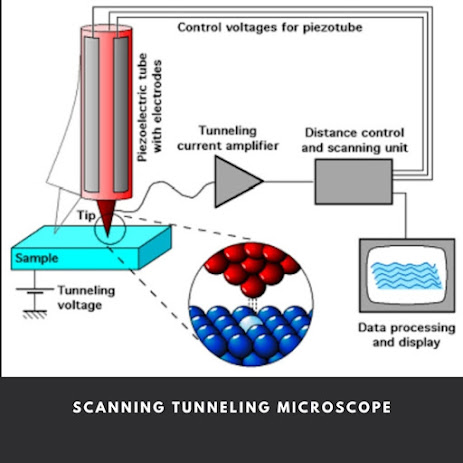
Construction and Working
STM utilizes a tip mode tungsten metal or platinum. Iridium alloy where at the end of tip there is only are custom of material. The scanner tip is attached to a piezoelectric tube scanner. By adjusting the voltage in the piezoelectric element, the distance between the tip and the surface can be regulated piezoelectric crystals expand and contract depending on the voltage applied to them and this principle is used to control the horizontal position x, y and the Height z of the scanning tip.
When tunneling voltage is applied between tip and sample, electron starts tunneling between tip and sample creating a weak electric current which can be amplified by tunneling current amplifier and can be measured. The tip is scanned across the sample to obtained to 3-D topographic image of sample surface on computer screen.
Modes of operation
There are 2 modes of operation of STM.
Constant current imaging
A fixed mechanism is used which provides a constant current while a constant voltage is applied between the sample and the tip. As the tip scans over the sample, the vertical position of the tip is altered to maintain the constant separation.
Constant Height imaging
In this mode the height of the probe tip from the surface of the sample is kept constant, so in this case by studying the current variations. we can construct the surface structure.

0 Comments
Do not share irrelevant messages.